Preparando MOJI
This is an interactive problem.
Little Dormi was faced with an awkward problem at the carnival: he has to guess the edges of an unweighted tree of $$$n$$$ nodes! The nodes of the tree are numbered from $$$1$$$ to $$$n$$$.
The game master only allows him to ask one type of question:
Additionally, to make the game unfair challenge Little Dormi the game master will allow at most $$$\lceil\frac{n}{2}\rceil$$$ questions, where $$$\lceil x \rceil$$$ denotes the smallest integer greater than or equal to $$$x$$$.
Faced with the stomach-churning possibility of not being able to guess the tree, Little Dormi needs your help to devise a winning strategy!
Note that the game master creates the tree before the game starts, and does not change it during the game.
After taking input, you may make at most $$$\lceil\frac{n}{2}\rceil$$$ queries. Each query is made in the format "? r", where $$$r$$$ is an integer $$$1 \le r \le n$$$ that denotes the node you want to pick for that query.
You will then receive $$$n$$$ space separated integers $$$d_1, d_2, \ldots, d_n$$$, where $$$d_i$$$ is the length of the shortest path from node $$$r$$$ to $$$i$$$, followed by a newline.
After printing a query do not forget to output end of line and flush the output. Otherwise, you will get Idleness limit exceeded. To do this, use:
If at any point you make an invalid query or try to make more than $$$\lceil \frac{n}{2} \rceil$$$ queries, the interaction will terminate immediately and you will receive a Wrong Answer verdict.
Hacks
To hack a solution, use the following format.
The first line contains the integer $$$n$$$ ($$$2 \le n \le 2\,000$$$).
The next $$$n−1$$$ lines contain two integers $$$u$$$ and $$$v$$$ ($$$1 \le u,v \le n$$$) denoting an edge between $$$u$$$ and $$$v$$$ ($$$u \neq v$$$). These $$$n-1$$$ edges must form a tree.
The first line of input contains the integer $$$n$$$ ($$$2 \le n \le 2\,000$$$), the number of nodes in the tree.
You will then begin interaction.
When your program has found the tree, first output a line consisting of a single "!" followed by $$$n-1$$$ lines each with two space separated integers $$$a$$$ and $$$b$$$, denoting an edge connecting nodes $$$a$$$ and $$$b$$$ ($$$1 \le a, b \le n$$$). Once you are done, terminate your program normally immediately after flushing the output stream.
You may output the edges in any order and an edge $$$(a,b)$$$ is considered the same as an edge $$$(b,a)$$$. Answering is not considered as a query.
4 0 1 2 2 1 0 1 1
? 1 ? 2 ! 4 2 1 2 2 3
5 2 2 1 1 0
? 5 ! 4 5 3 5 2 4 1 3
Here is the tree from the first example.
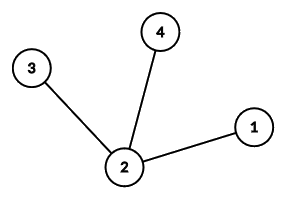
Notice that the edges can be output in any order.
Additionally, here are the answers for querying every single node in example $$$1$$$:
Below is the tree from the second example interaction.
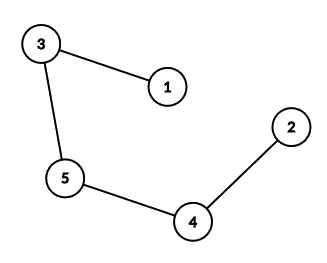
Lastly, here are the answers for querying every single node in example $$$2$$$: