Preparando MOJI
Petya wrote a programme on C++ that calculated a very interesting function f(n). Petya ran the program with a certain value of n and went to the kitchen to have some tea. The history has no records concerning how long the program had been working. By the time Petya returned, it had completed the calculations and had the result. However while Petya was drinking tea, a sly virus managed to destroy the input file so that Petya can't figure out for which value of n the program was run. Help Petya, carry out the inverse function!
Mostly, the program consists of a function in C++ with the following simplified syntax:
The whitespaces in a operatorSequence are optional.
Thus, we have a function, in which body there are two kinds of operators. There is the operator "return arithmExpr;" that returns the value of the expression as the value of the function, and there is the conditional operator "if (logicalExpr) return arithmExpr;" that returns the value of the arithmetical expression when and only when the logical expression is true. Guaranteed that no other constructions of C++ language — cycles, assignment operators, nested conditional operators etc, and other variables except the n parameter are used in the function. All the constants are integers in the interval [0..32767].
The operators are performed sequentially. After the function has returned a value other operators in the sequence are not performed. Arithmetical expressions are performed taking into consideration the standard priority of the operations. It means that first all the products that are part of the sum are calculated. During the calculation of the products the operations of multiplying and division are performed from the left to the right. Then the summands are summed, and the addition and the subtraction are also performed from the left to the right. Operations ">" (more), "<" (less) and "==" (equals) also have standard meanings.
Now you've got to pay close attention! The program is compiled with the help of 15-bit Berland C++ compiler invented by a Berland company BerSoft, that's why arithmetical operations are performed in a non-standard way. Addition, subtraction and multiplication are performed modulo 32768 (if the result of subtraction is negative, then 32768 is added to it until the number belongs to the interval [0..32767]). Division "/" is a usual integer division where the remainder is omitted.
Examples of arithmetical operations:
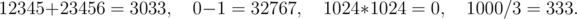
Guaranteed that for all values of n from 0 to 32767 the given function is performed correctly. That means that:
1. Division by 0 never occures.
2. When performing a function for the value n = N recursive calls of the function f may occur only for the parameter value of 0, 1, ..., N - 1. Consequently, the program never has an infinite recursion.
3. As the result of the sequence of the operators, the function always returns a value.
We have to mention that due to all the limitations the value returned by the function f is independent from either global variables or the order of performing the calculations of arithmetical expressions as part of the logical one, or from anything else except the value of n parameter. That's why the f function can be regarded as a function in its mathematical sense, i.e. as a unique correspondence between any value of n from the interval [0..32767] and a value of f(n) from the same interval.
Given the value of f(n), and you should find n. If the suitable n value is not unique, you should find the maximal one (from the interval [0..32767]).
The first line has an integer f(n) from the interval [0..32767]. The next lines have the description of the function f. In the description can be found extra spaces and line breaks (see the examples) which, of course, can’t break key words int, if, return and numbers. The size of input data can’t exceed 100 bytes.
Output a single number — the answer to the problem. If there’s no answer, output "-1" (without quotes).
17
int f(int n)
{
if (n < 100) return 17;
if (n > 99) return 27;
}
99
13
int f(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
return f(n - 1) + 1;
}
13
144
int f(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return n;
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}
24588