Preparando MOJI
Optimizing the amount of data transmitted via a network is an important and interesting part of developing any network application.

In one secret game developed deep in the ZeptoLab company, the game universe consists of n levels, located in a circle. You can get from level i to levels i - 1 and i + 1, also you can get from level 1 to level n and vice versa. The map of the i-th level description size is ai bytes.
In order to reduce the transmitted traffic, the game gets levels as follows. All the levels on the server are divided into m groups and each time a player finds himself on one of the levels of a certain group for the first time, the server sends all levels of the group to the game client as a single packet. Thus, when a player travels inside the levels of a single group, the application doesn't need any new information. Due to the technical limitations the packet can contain an arbitrary number of levels but their total size mustn't exceed b bytes, where b is some positive integer constant.
Usual situation is that players finish levels one by one, that's why a decision was made to split n levels into m groups so that each group was a continuous segment containing multiple neighboring levels (also, the group can have two adjacent levels, n and 1). Specifically, if the descriptions of all levels have the total weight of at most b bytes, then they can all be united into one group to be sent in a single packet.
Determine, what minimum number of groups do you need to make in order to organize the levels of the game observing the conditions above?
As developing a game is a long process and technology never stagnates, it is yet impossible to predict exactly what value will take constant value b limiting the packet size when the game is out. That's why the developers ask you to find the answer for multiple values of b.
The first line contains two integers n, q (2 ≤ n ≤ 106, 1 ≤ q ≤ 50) — the number of levels in the game universe and the number of distinct values of b that you need to process.
The second line contains n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the sizes of the levels in bytes.
The next q lines contain integers bj (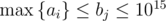 ), determining the values of constant b, for which you need to determine the answer.
), determining the values of constant b, for which you need to determine the answer.
For each value of kj from the input print on a single line integer mj (1 ≤ mj ≤ n), determining the minimum number of groups to divide game levels into for transmission via network observing the given conditions.
6 3
2 4 2 1 3 2
7
4
6
2
4
3
In the test from the statement you can do in the following manner.