Preparando MOJI
Dr. Evil is interested in math and functions, so he gave Mahmoud and Ehab array a of length n and array b of length m. He introduced a function f(j) which is defined for integers j, which satisfy 0 ≤ j ≤ m - n. Suppose, ci = ai - bi + j. Then f(j) = |c1 - c2 + c3 - c4... cn|. More formally, 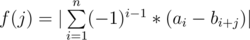 .
.
Dr. Evil wants Mahmoud and Ehab to calculate the minimum value of this function over all valid j. They found it a bit easy, so Dr. Evil made their task harder. He will give them q update queries. During each update they should add an integer xi to all elements in a in range [li;ri] i.e. they should add xi to ali, ali + 1, ... , ari and then they should calculate the minimum value of f(j) for all valid j.
Please help Mahmoud and Ehab.
The first line contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n ≤ m ≤ 105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — number of elements in a, number of elements in b and number of queries, respectively.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an. ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — elements of a.
The third line contains m integers b1, b2, ..., bm. ( - 109 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — elements of b.
Then q lines follow describing the queries. Each of them contains three integers li ri xi (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ n, - 109 ≤ x ≤ 109) — range to be updated and added value.
The first line should contain the minimum value of the function f before any update.
Then output q lines, the i-th of them should contain the minimum value of the function f after performing the i-th update .
5 6 3
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 1 10
1 1 -9
1 5 -1
0
9
0
0
For the first example before any updates it's optimal to choose j = 0, f(0) = |(1 - 1) - (2 - 2) + (3 - 3) - (4 - 4) + (5 - 5)| = |0| = 0.
After the first update a becomes {11, 2, 3, 4, 5} and it's optimal to choose j = 1, f(1) = |(11 - 2) - (2 - 3) + (3 - 4) - (4 - 5) + (5 - 6) = |9| = 9.
After the second update a becomes {2, 2, 3, 4, 5} and it's optimal to choose j = 1, f(1) = |(2 - 2) - (2 - 3) + (3 - 4) - (4 - 5) + (5 - 6)| = |0| = 0.
After the third update a becomes {1, 1, 2, 3, 4} and it's optimal to choose j = 0, f(0) = |(1 - 1) - (1 - 2) + (2 - 3) - (3 - 4) + (4 - 5)| = |0| = 0.